


A Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC) is akin to a banking company and engaged in the business of providing loans, accepting deposits (only certain NBFCs), leasing, hire purchase, acquisition of stocks, insurance, etc.
In accordance with the RBI Act of 1934, supervises the process by which companies are registered under the Companies Act. The NBFCs play a vital role in the Indian economy. They facilitate financial operations, and they fill in for traditional banks when they are unable to extend loans or advances.
Moreover, the majority of deposits are accepted by non-banking finance corporations (NBFCs) according to prescribed schemes and agreements. Depositors can choose to pay in one lump sum or in instalments.
The RBI regulates and supervises the NBFCs in accordance to the RBI Act of 1934. According to Section 45-IA of the RBI Act, an NBFC cannot start or continue business in India without a NBFC registration certificate.
In India, the RBI is the only authority that can issue NBFC certificates. In recent years, RBI has simplified policies and regulations for the NBFCs. This makes the process easier to obtain a registration certificate.
NBFCs, or Non-Banking Financial Companies, are corporate entities registered under the Companies Act 2013 regulations. The Reserve Bank of India is responsible for regulating NBFCs.
NBFCs are still involved in providing services such as loans and advances, and acquiring shares, equities and debts issued either by the local or national government. Further, NBFCs differ from commercial banks and cooperative banks.
According to Section 45-IA in the RBI Act, 1934, a company wishing to register as an NBFC must meet the following requirements:
The following activities are not considered NBFCs in India.
|
Criteria for Comparison |
Non-banking Financial Corporation |
BANK |
|
Act of Regulation |
Companies Act, 2013 |
Banking Regulation Act of 1949 |
|
Demand Deposits |
Demand Deposits are not Acceptable |
Can accept demand deposit |
|
Drawing a Cheque |
The cheque cannot be drawn by itself |
You can draw and issue a cheque |
|
Deposit Insurance Facility |
This facility does not accept NBFC deposits |
The facility is open to all bank depositors |
|
Asset restructuring |
|
No Entry |
|
Maintaining Reserve Ratios |
No Mandatory |
The reserve ratio must be maintained |
|
Loan sanction |
Faster and easier |
Comparatively rigid |
|
Product Offering |
Most Property Loans |
There are many types of loans |
|
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) |
Allowable up to a limit |
Permissible |
|
Statutory Reserve Ratio |
The 15% SLR is a must for deposit-taking NBFCs |
Maintaining SLR as a requirement |
Below are some specific roles and functions that NBFCs in India perform:
The financial industry has evolved with the advent of technology. It is now able to upgrade its business and provide various benefits for the Indian economy. Below are some advantages of Fintech-based NBFC models.
RBI can cancel a NBFC registration application for any of the following reasons.
NBFC stands for Non-Banking Financial Company. It is a type of financial institution that operates without a banking license and provides financial services such as loans, investments, and other financial products and services. It is regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and are required to comply with various regulations and guidelines issued by the RBI.
Registering an NBFC in India offers several benefits, including increased credibility and trustworthiness in the eyes of customers and investors, as well as the ability to engage in a wide range of financial activities such as lending, leasing, investment, and insurance. NBFCs can also raise funds and lending capacity through various sources such as fixed deposits, bonds, and commercial papers. Additionally, being an NBFC provides more flexibility, and interest rates can be higher than those offered by banks, leading to increased profit margins. Finally, NBFCs can play a crucial role in promoting financial inclusion by providing loans and other financial services to underserved segments of society, such as low-income households, small businesses, and rural areas.
In India, registration as a Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC) is open to various entities, including companies registered under the Companies Act of 2013 or its predecessor, the Companies Act of 1956, co-operative societies whose principal business is finance-related activities and registered under any law in force in India, and partnership firms, limited liability partnerships (LLPs), or any other association of persons engaged in the business of providing finance-related activities.
These entities are eligible to apply for registration as NBFCs, subject to compliance with relevant regulations and guidelines laid down by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
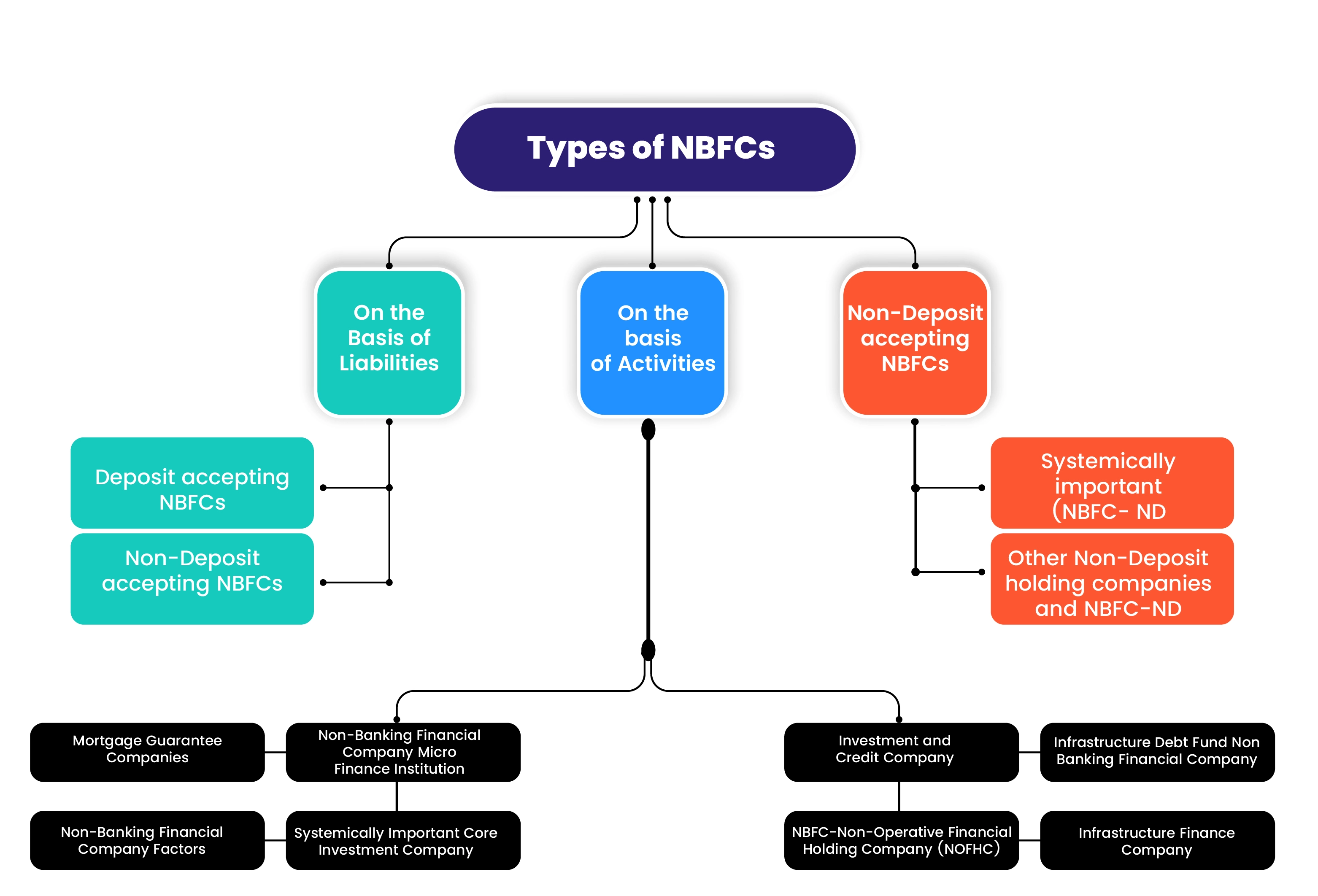
India has a diverse range of Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs), each with their unique set of rules and regulations. The different types of NBFCs include Asset Finance Companies (AFC), Investment Companies (IC), Loan Companies (LC), Infrastructure Finance Companies (IFC), Systemically Important Core Investment Companies (CIC-ND-SI), Microfinance Institutions (MFI), Non-Banking Financial Companies-Factors (NBFC-Factors), and Non-Banking Financial Companies-Micro Finance Institutions (NBFC-MFIs).
These NBFCs cater to various segments of the economy and offer financial services to individuals and businesses. Each NBFC is regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and must adhere to the guidelines and regulations set by the RBI.
An NBFC (Non-Banking Financial Company) is a financial institution that provides financial services like loans, credit facilities, investments, and other financial products, but it cannot accept deposits from the public. In contrast, a bank is a financial institution that accepts deposits from the public and provides a range of financial services. Banks also have additional privileges, such as issuing cheques, providing checking and savings accounts, and providing payment and settlement services. Additionally, banks are more heavily regulated than NBFCs, and are subject to specific regulations under the Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
Non-compliance with NBFC regulations in India can lead to severe consequences, including penalties and legal action by the regulatory authority, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). The penalties for non-compliance can result in monetary fines, cancellation of registration, and even criminal prosecution. The severity of the violation determines the amount of the penalty, which can range from a few lakh rupees to several crores.
Apart from imposing penalties, the RBI can take additional measures like restricting the NBFC's business operations, removing its directors, or appointing a management team to run the company. Therefore, NBFCs operating in India must comply with the regulatory framework to avoid any adverse actions by the RBI.
























































Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *